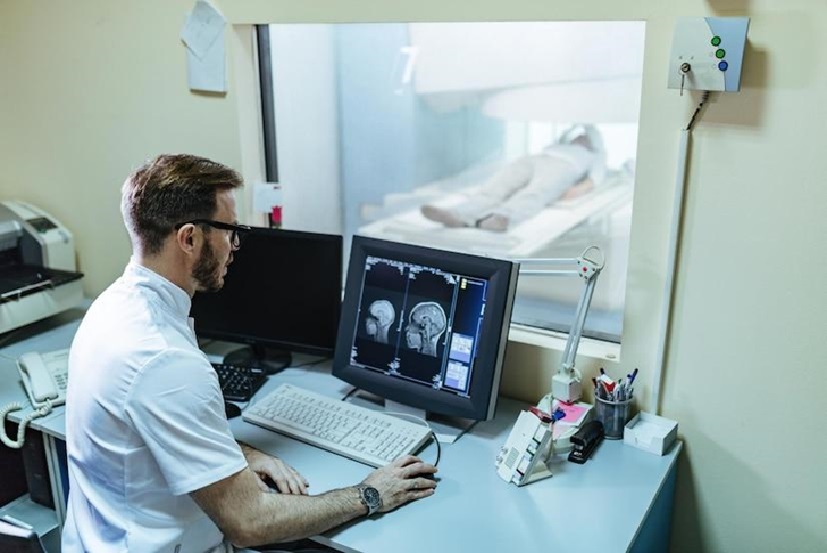
MRI scans have revolutionized brain surgery by providing precise, detailed imaging of brain structures. These scans help identify tumors, aneurysms, and areas of damage or inflammation, enabling accurate diagnosis and surgical planning. By guiding surgeries for conditions like brain tumors, epilepsy, and Parkinson’s disease, MRI reduces invasiveness, minimizes risks, and improves outcomes, transforming neurological care and enhancing patients’ lives.
What Is An MRI Scan?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive diagnostic tool that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of internal body structures, especially the brain. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI avoids ionizing radiation, making it safer for repeated use. It works by aligning hydrogen atoms in the body with magnets and capturing signals as they return to their normal state, generating high-resolution images in multiple planes.
MRI is essential for diagnosing neurological disorders and detecting abnormalities like lesions, tumors, or vascular issues. Advances like functional MRI (fMRI) add insights into brain activity by tracking blood flow, aiding diagnosis and treatment planning. This technology has become indispensable in modern neurology, offering unparalleled imaging precision.
Importance Of MRI Scans In Diagnosing Neurological Disorders
MRI scans are invaluable for diagnosing neurological disorders, offering detailed imaging essential for assessing the brain’s complexity. Subtle symptoms of conditions like multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s, or dementia can be challenging to interpret, but MRI helps identify structural and functional changes, enabling early detection and intervention.
MRI also aids in differentiating between conditions, such as distinguishing a tumor from a stroke, by providing detailed insights into abnormalities like masses or inflammation. This precision allows for accurate diagnoses and guides effective treatment planning, significantly improving patient outcomes. For detailed information, visit Tellica Imaging (https://tellicaimaging.com/ ) for high-quality imaging services.
Common Neurological Disorders Diagnosed Using MRI Scans
MRI scans are crucial in diagnosing and managing neurological disorders by providing detailed insights into the brain and central nervous system. They help determine brain tumor size, location, and operability, guiding tailored surgical plans. In multiple sclerosis (MS), MRI detects characteristic brain and spinal cord lesions, monitors disease progression, and informs treatment adjustments.
MRI is also vital for stroke diagnosis, distinguishing between ischemic and hemorrhagic events and assessing affected brain areas to guide immediate care and rehabilitation. Conditions like epilepsy, Parkinson’s, and neurodegenerative diseases further benefit from MRI diagnostics, underscoring its importance in modern neurology.
How MRI Scans Guide Brain Surgery
MRI scans in brain surgery have significantly improved precision and outcomes. Intraoperative MRI provides real-time images during operations, helping surgeons make informed decisions. For tumor removal, it confirms complete resection and detects residual cancerous cells, reducing the need for additional surgeries.
MRI also aids in epilepsy surgeries by pinpointing seizure-causing brain regions, enabling accurate and targeted interventions while preserving vital functions. By visualizing critical structures like blood vessels and functional brain areas, MRI minimizes damage to healthy tissue, enhancing patient safety and surgical success. Ongoing advancements continue to refine its role in neurosurgery.
Preparing For An MRI Scan
Preparing for an MRI scan is crucial to ensure accurate results and a smooth procedure. Patients should discuss their medical history with their healthcare provider, including any health conditions before surgery, and consult with brain surgery professionals as needed. Fasting may be required for contrast-enhanced MRIs, where a contrast agent highlights specific brain structures.
Patients should wear comfortable, metal-free clothing or change into a gown and leave valuables at home to prevent interference from the MRI’s powerful magnets. Understanding the procedure and its purpose can help alleviate anxiety and contribute to a successful imaging experience.
The Process Of Getting An MRI Scan
The MRI process involves several key steps to ensure safety and accuracy. Upon arrival, patients complete paperwork and have a brief consultation with the radiologic technologist, who explains the procedure and reviews medical history.
Patients then lie on a table that slides into the MRI machine, resembling a large cylinder. Staying still is crucial to avoid blurry images. Headphones or earplugs may be provided to reduce noise. The scan usually lasts 30 minutes to an hour, with a series of pictures taken. The technologist may ask for breath-holding or position changes. Afterward, patients can resume normal activities, and a radiologist will analyze the images for the referring physician.
Understanding MRI Scan Results
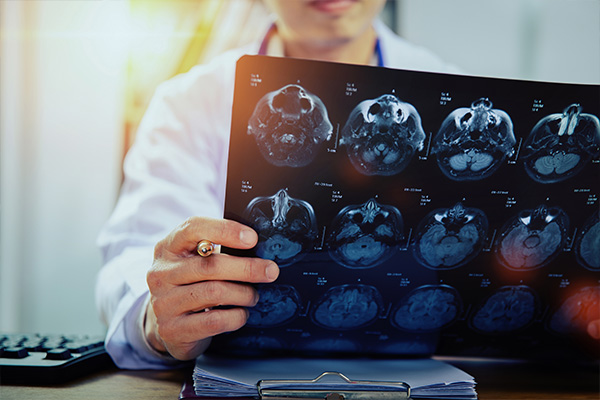
Interpreting MRI results is a crucial step in diagnosing neurological conditions. After the scan, a radiologist analyzes the images to identify abnormalities like tumors, lesions, or structural changes in the brain. The findings are compiled into a report and sent to the referring physician for evaluation.
Patients may feel anxious while waiting but understanding potential outcomes can help. Abnormalities, such as tumors, are described by size, location, and characteristics, which may indicate whether they are benign or malignant.
If needed, the physician will discuss the results and recommend further tests, treatments, or referrals. Open communication with healthcare providers is essential for understanding the condition and next steps.
Risks And Limitations Of MRI Scans
MRI scans are a valuable diagnostic tool but have risks and limitations. Metal implants, such as pacemakers or surgical clips, can be affected by the MRI’s magnetic fields, so it’s essential to inform healthcare providers. Some patients may also experience anxiety or claustrophobia, but open MRIs or sedation can help. Additionally, MRI may not effectively visualize bones, so other imaging techniques like CT scans or ultrasounds may be needed. Understanding these limitations helps patients make informed decisions.
Conclusion: The Role Of MRI Scans In Improving Brain Surgery Outcomes
In summary, MRI scans have revolutionized the diagnosis and treatment of neurological disorders. They provide detailed brain images, helping professionals identify abnormalities and guide surgeries with precision, reducing risks and improving outcomes. As medical technology advances, MRI’s role in neurology and brain surgery will continue to grow, offering more sophisticated techniques for better diagnostic accuracy and treatment. For patients, understanding the importance of MRI scans can enhance their engagement in the healthcare process, providing reassurance and hope for the future of neurological care.